The Quarterly Issues/Programs List (“Quarterly List”) for each of the First Quarter and Second Quarter of 2020 must be placed in stations’ Public Inspection Files by July 10, 2020, reflecting information for the months of January through March, and April through June, respectively. The deadline for the First Quarterly Issues/Programs List was extended to July 10 to coincide with the filing of the Second Quarterly Issues/Programs List, thereby allowing stations three additional months in light of the challenges caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Content of the Quarterly List
The FCC requires each broadcast station to air a reasonable amount of programming responsive to significant community needs, issues, and problems as determined by the station. The FCC gives each station the discretion to determine which issues facing the community served by the station are the most significant and how best to respond to them in the station’s overall programming.
To demonstrate a station’s compliance with this public interest obligation, the FCC requires the station to maintain and place in the Public Inspection File a Quarterly List reflecting the “station’s most significant programming treatment of community issues during the preceding three month period.” By its use of the term “most significant,” the FCC has noted that stations are not required to list all responsive programming, but only that programming which provided the most significant treatment of the issues identified.
Given that program logs are no longer mandated by the FCC, the Quarterly Lists may be the most important evidence of a station’s compliance with its public service obligations. The lists also provide important support for the certification of Class A television station compliance discussed below. We therefore urge stations not to “skimp” on the Quarterly Lists, and to err on the side of over-inclusiveness. Otherwise, stations risk a determination by the FCC that they did not adequately serve the public interest during their license term. Stations should include in the Quarterly Lists as much issue-responsive programming as they feel is necessary to demonstrate fully their responsiveness to community needs. Taking extra time now to provide a thorough Quarterly List will help reduce risk at license renewal time.
The FCC has repeatedly emphasized the importance of the Quarterly Lists and often brings enforcement actions against stations that do not have complete Quarterly Lists in their Public Inspection File or which have failed to timely upload such lists when due. The FCC’s base fine for missing Quarterly Lists is $10,000.
Preparation of the Quarterly List
The Quarterly Lists are normally required to be placed in the Public Inspection File by January 10, April 10, July 10, and October 10 of each year. Because of the unusual extension granted this year due to COVID-19, however, the Quarterly Lists covering the First and Second Quarters of 2020 are both required to be placed in stations’ Public Inspection Files by July 10, 2020, covering the periods from January 1, 2020 through March 31, 2020, and April 1, 2020 through June 30, 2020, respectively.
Stations should keep the following in mind:
- Stations should maintain routine outreach to the community to learn of various groups’ perceptions of community issues, problems, and needs. Stations should document the contacts they make and the information they learn. Letters to the station regarding community issues should be made a part of the station’s database.
- There should be procedures in place to organize the information that is gathered and bring it to the attention of programming staff with a view towards producing and airing programming that is responsive to significant community issues. This procedure and its results should be documented.
- Stations should ensure that there is some correlation between the station’s contacts with the community, including letters received from the public, and the issues identified in their Quarterly Lists. A station should not overlook significant issues. In a contested license renewal proceeding, while the station may consider what other stations in the market are doing, each station will have the burden of persuading the FCC that it acted “reasonably” in deciding which issues to address and how.
- Stations should not specify an issue for which no programming is identified. Conversely, stations should not list programs for which no issue is specified.
- Under its former rules in this area, the FCC required a station to list five to ten issues per quarter. While that specific rule has been eliminated, the FCC has noted that such an amount will likely demonstrate compliance with the station’s issue-responsive programming obligations. However, the FCC has indicated that licensees may choose to concentrate on fewer than five issues if they cover them in considerable depth. Conversely, the FCC has noted that broadcasters may seek to address more than ten issues in a given quarter, due perhaps to program length, format, etc.
- The Quarterly List should reflect a wide variety of significant issues. For example, five issues affecting the Washington, DC community might be: (1) the fight over statehood for the District of Columbia; (2) fire code violations in DC school buildings; (3) clean-up of the Anacostia River; (4) reforms in the DC Police Department; and (5) proposals to increase the use of traffic cameras on local streets. The issues should change over time, reflecting the station’s ongoing ascertainment of changing community needs and concerns.
- Accurate and complete records of which programs were used to discuss or treat which issues should be preserved so that the job of constructing the Quarterly List is made easier. The data retained should help the station identify the programs that represented the “most significant treatment” of issues (e.g., duration, depth of presentation, frequency of broadcast, etc.).
- The listing of “most significant programming treatment” should demonstrate a wide variety in terms of format, duration (long-form and short-form programming), source (locally produced is presumptively the best), time of day (times of day when the programming is likely to be effective), and days of the week. Stations should not overlook syndicated and network programming as ways to address issues.
- Stations should prepare each Quarterly List in time for it to be placed in their Public Inspection File on or before the due date. If the deadline is not met, stations should give the true date when the document was placed in the Public Inspection File and explain its lateness.
- Stations should show that their programming commitment covers all three months within each quarter.
These are just some suggestions that can assist stations in meeting their obligations under the FCC’s rules. The requirement to list programs providing the most significant treatment of issues may persuade a station to review whether its programming truly and adequately educates the public about community concerns.
Attached is a sample format for a “Quarterly Issues/Programs List” to assist stations in creating their own Quarterly List. Please do not hesitate to contact the attorneys in the Communications Practice for specific advice on how to ensure your compliance efforts in this area are adequate.
Class A Television Stations Only
Class A television stations must certify that they continue to meet the FCC’s eligibility and service requirements for Class A television status under Section 73.6001 of the FCC’s Rules. While the relevant subsection of the Public Inspection File rule, Section 73.3526(e)(17), does not specifically state when this certification should be prepared and placed in the Public Inspection File, we believe that since Section 73.6001 assesses compliance on a quarterly basis, the prudent course for Class A television stations is to place the Class A certification in the Public Inspection File on a quarterly basis as well.
Sample Quarterly Issues/Programs List [1]
Below is a list of some of the significant issues responded to by Station [call sign], [community of license], [state of license], along with the most significant programming treatment of those issues for the period [date] to [date]. This list is by no means exhaustive. The order in which the issues appear does not reflect any priority or significance.
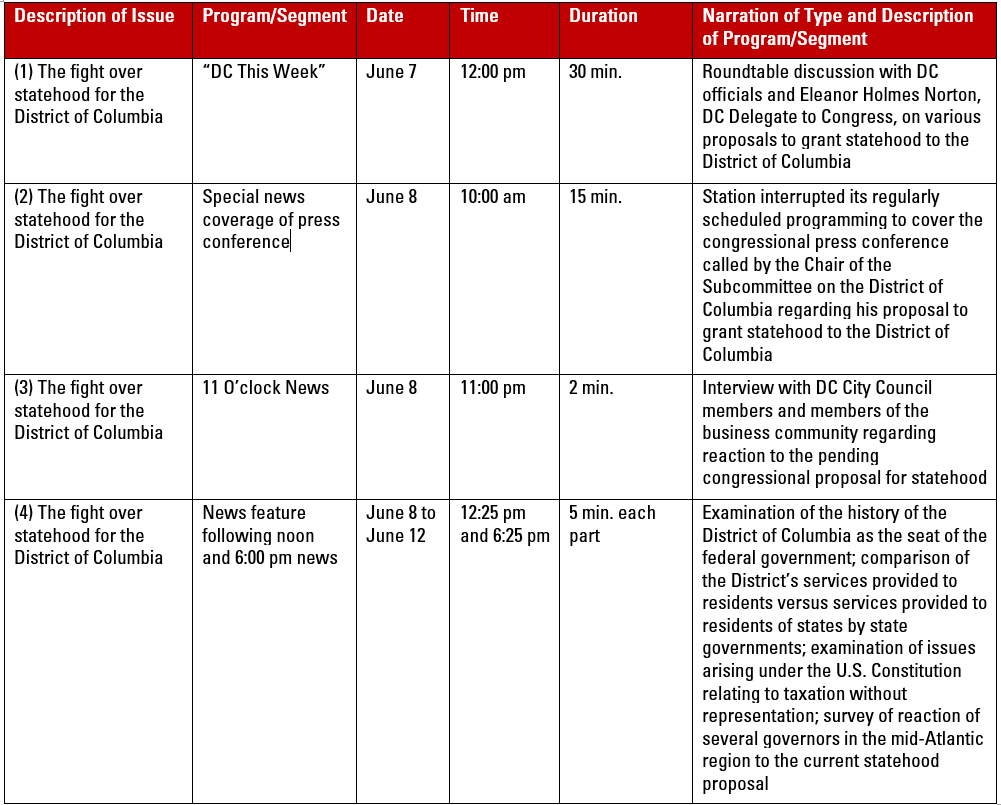
[1] This sample illustrates the treatment of one issue only.
A PDF version of this article can be found at First and Second Quarter 2020 Issues/Programs Lists Advisory for Broadcast Stations.
 Comm Law Center
Comm Law Center


